Description
Research Applications:
Mitochondrial Function and Energy Metabolism
NAD⁺ is an essential redox cofactor in mitochondrial energy production, particularly in oxidative phosphorylation. It shuttles electrons from glycolysis and the TCA cycle to the electron transport chain, enabling ATP generation [1]. Research using NAD⁺ focuses on its role in mitochondrial bioenergetics and cellular adaptation under energetic stress.
Depletion of NAD⁺ levels is frequently observed in aged or metabolically stressed cells, making it a target in studies of mitochondrial dysfunction, senescence, and metabolic disorders.
Sirtuin Activation and Epigenetic Regulation
NAD⁺ is a required co-substrate for sirtuin deacetylases (SIRT1–SIRT7), which are involved in DNA repair, chromatin remodeling, and gene expression [2]. These enzymes regulate cellular longevity, inflammation, and metabolic adaptation, making NAD⁺ supplementation a critical variable in aging and epigenetic studies.
Studies often explore how NAD⁺ influences SIRT1-mediated pathways to improve DNA stability, reduce histone acetylation, and modulate transcriptional activity under stress conditions.
DNA Repair and PARP Function
NAD⁺ is also a substrate for poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases (PARPs), which mediate DNA damage response and repair mechanisms. When DNA strand breaks occur, PARP enzymes consume NAD⁺ to signal for repair machinery, especially under oxidative stress or genotoxic insult [3].
In research models, excessive PARP activation can lead to NAD⁺ depletion and subsequent ATP loss, contributing to cell death. Thus, NAD⁺ is studied in contexts of genomic stability, neurodegeneration, and cell survival signaling.
Immunometabolism and Inflammatory Regulation
Recent research links NAD⁺ to immune cell regulation, particularly via CD38 and SIRT1 pathways in macrophages and T-cells. NAD⁺ modulates pro-inflammatory cytokine expression and T-cell function, making it a point of interest in immunometabolic research [4].
Studies are exploring how NAD⁺ levels influence cellular redox states and inflammatory gene transcription, especially in chronic inflammatory or autoimmune models.


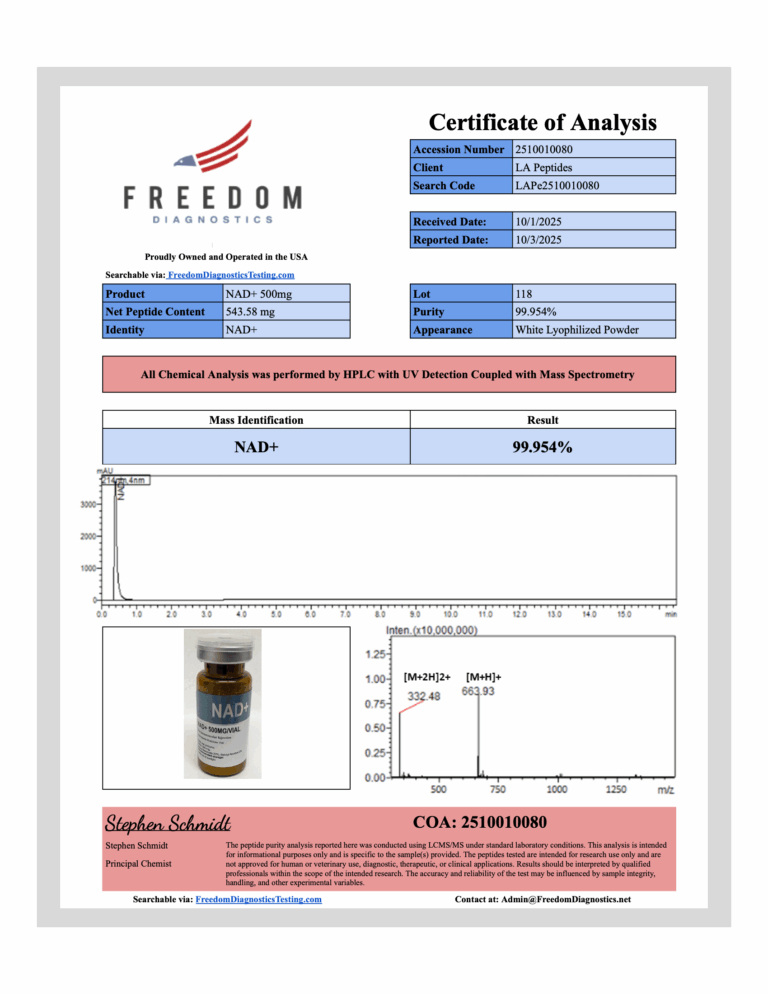










There are no reviews yet.