Description
Comprehensive PubChem-Based Research Overview
Molecular Identity & Structure
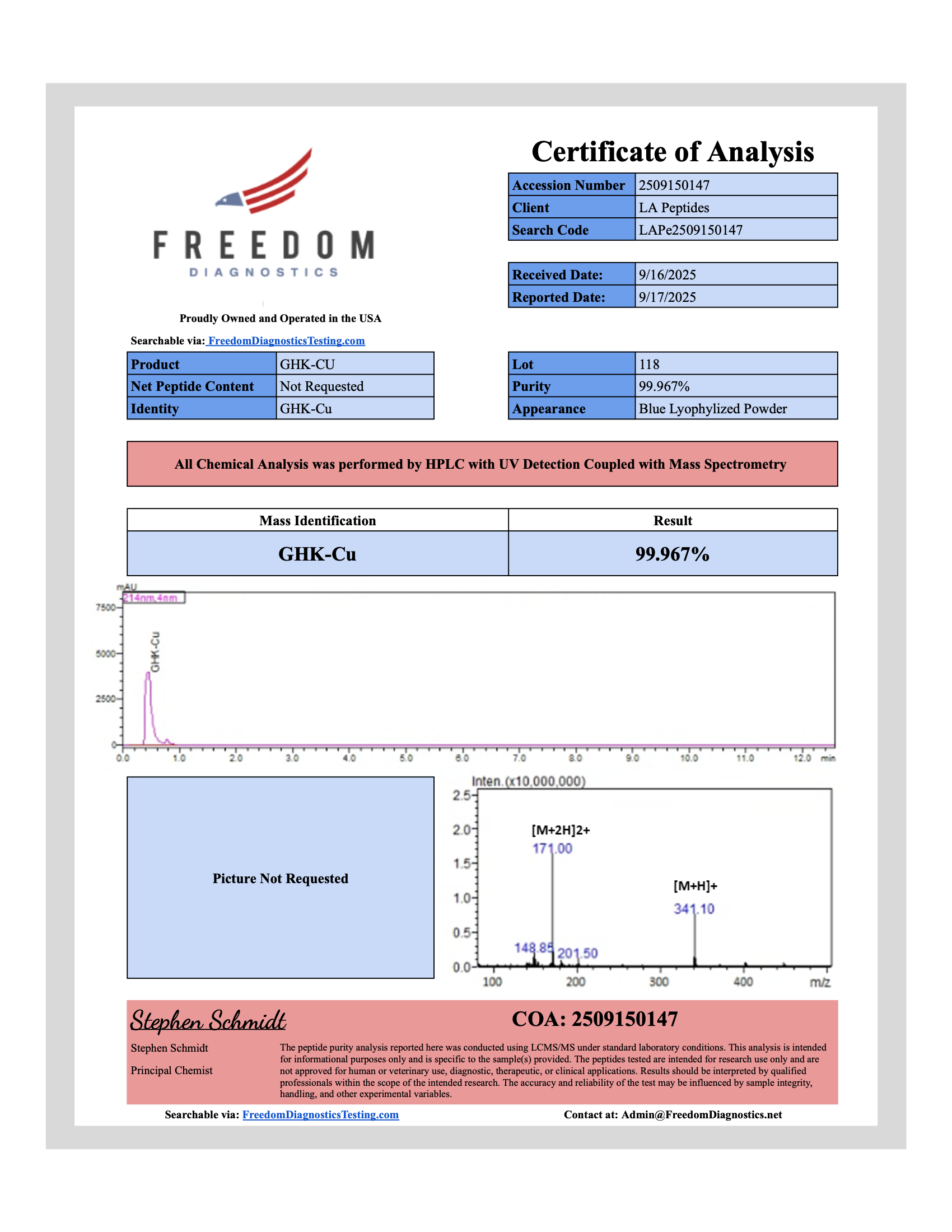
GHK-Cu is the copper(II) chelate of the tripeptide glycyl-histidyl-lysine. PubChem records its molecular formula as C14H24CuN6O4 and molecular weight ~340.9 g/mol [1]. Its structure enables high-affinity binding of Cu²⁺ ions, stabilizing the tripeptide and supporting biochemical studies of metal–peptide interactions.
Copper Transport & Metalloprotein Regulation
As a copper-binding complex, GHK-Cu facilitates laboratory modeling of copper transport and distribution. PubChem annotations note its use in experimental systems studying lysyl oxidase activity, superoxide dismutase regulation, and copper-dependent enzymatic pathways [1]. These studies help clarify metal-ion bioavailability and metalloprotein activation.
Extracellular Matrix & Collagen Research
PubChem literature links describe the peptide’s ability to modulate extracellular matrix metabolism [1]. In vitro assays frequently measure collagen synthesis, fibronectin expression, and matrix metalloproteinase activity following GHK-Cu exposure. Researchers employ these endpoints to better understand tissue remodeling, fibrosis models, and controlled wound-healing pathways.
Oxidative Stress & Antioxidant Studies
Through copper coordination, GHK-Cu contributes to studies of redox balance and reactive oxygen species (ROS) regulation. PubChem cites related antioxidant activity, allowing its use in mechanistic investigations of oxidative stress response and cellular defense against free radicals in controlled model systems [1].
Cellular Signaling & Gene Expression
Experimental evidence aggregated in PubChem demonstrates GHK-Cu’s effects on transcriptional networks related to growth factors, angiogenesis mediators, and inflammatory cytokines [1]. This makes it a useful chemical probe for evaluating copper-mediated signal transduction in cultured cells, without implying therapeutic use.











There are no reviews yet.