Description
Comprehensive PubChem-Based Research Overview
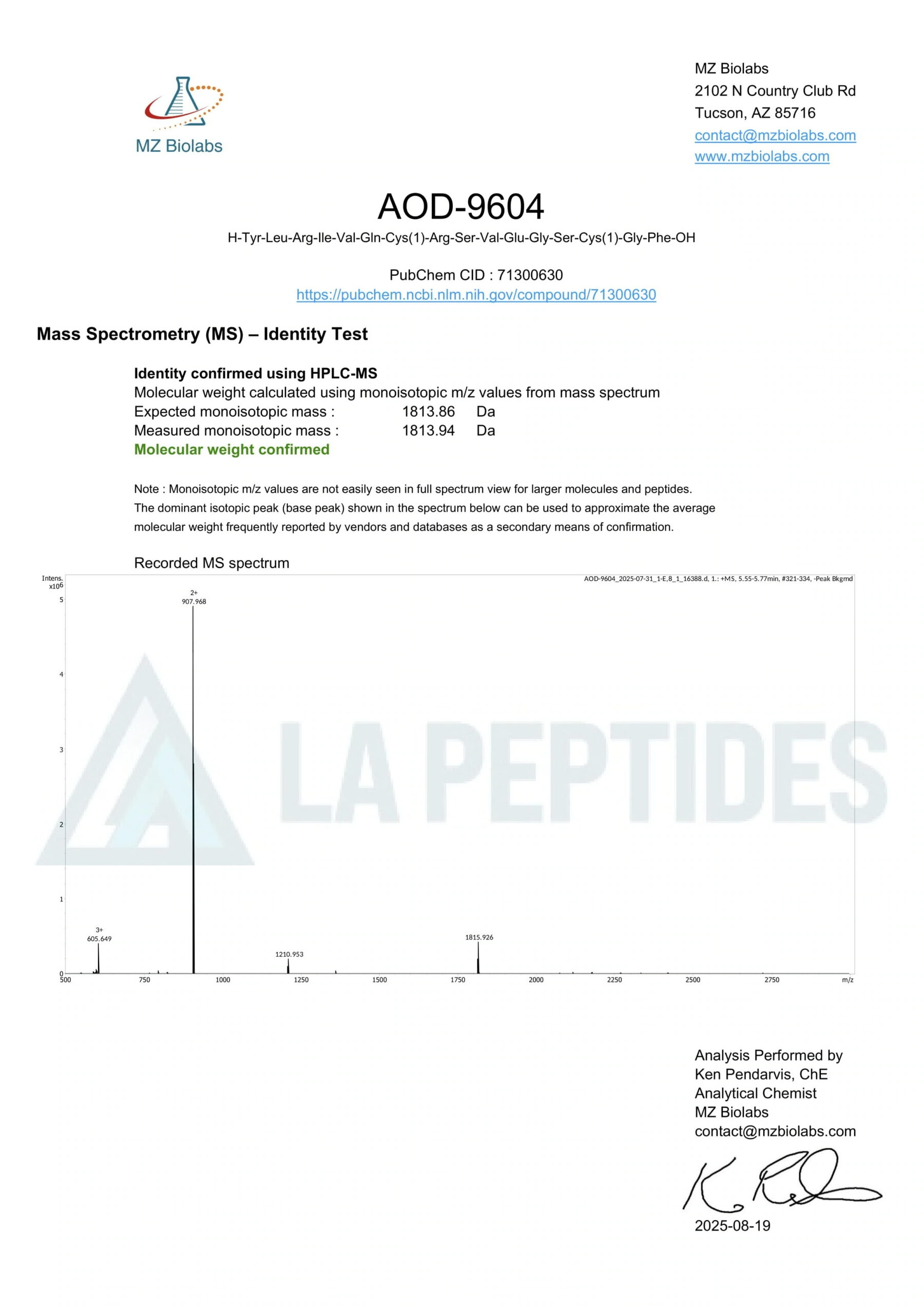
Molecular Identity & Structure
NAD⁺ is listed in PubChem as CID 5892, with the molecular formula C21H27N7O14P2 and a molecular weight of ~663.4 g/mol [1]. Structurally, it is a dinucleotide composed of an adenine mononucleotide and a nicotinamide mononucleotide linked through phosphate groups. This identity supports its use as a traceable coenzyme in metabolic assays.
Redox Biology & Enzymatic Research
PubChem annotations describe NAD⁺ as a critical cofactor in oxidoreductase reactions [1][2]. It functions as an electron acceptor in pathways including glycolysis, the tricarboxylic acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. In vitro, it is widely used to examine enzyme kinetics, electron transfer reactions, and metabolic flux.
Nasal Spray Format & Transport Models
In nasal spray preparation, NAD⁺ provides researchers with a format to study epithelial absorption, stability, and mucosal transport [2]. Laboratory use includes cell-based barrier models and ex vivo tissue assays to quantify transport efficiency compared to injectable or lyophilized forms.
Metabolic & Cellular Applications
- Mitochondrial studies: assessing NAD⁺/NADH ratios under varying conditions.
- Signal transduction research: probing sirtuin- and PARP-dependent pathways.
- Stress and aging models: quantifying NAD⁺ availability under oxidative or genotoxic stress.
All such applications are restricted to bench-scale laboratory use.
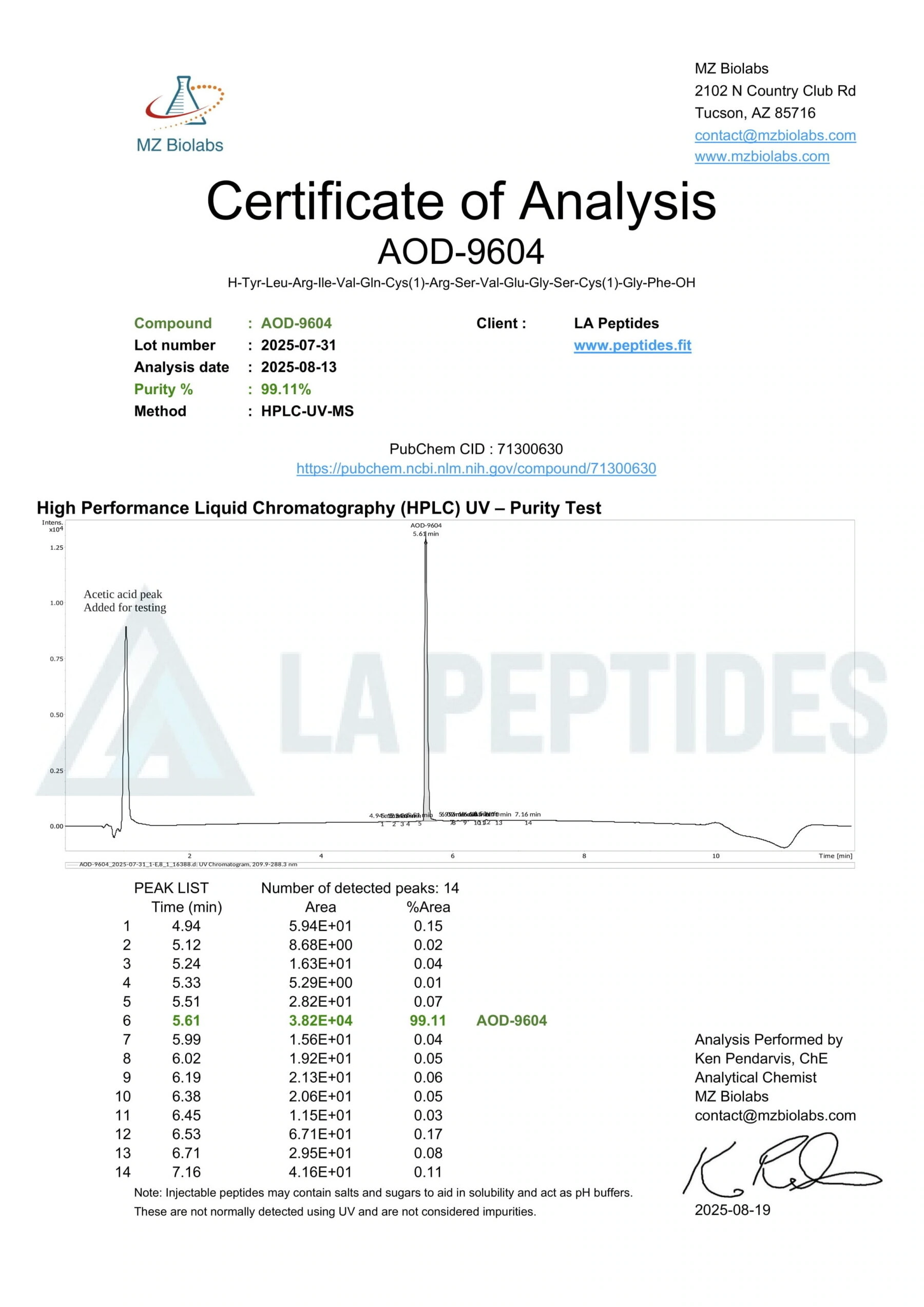
Data Traceability & QC Integration
PubChem provides registry identifiers, including CAS 53-84-9, structural files, and depositor data [1]. These support quality control, reproducibility across labs, and integration into screening platforms or metabolic pathway databases.










There are no reviews yet.